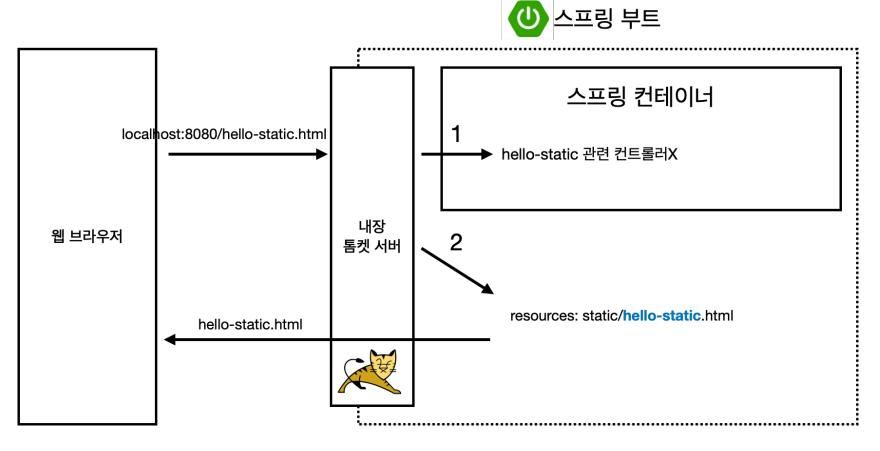
정적 컨텐츠
서버에서는 따로 하는 것 없이 그대로 웹 브라우저에 내려주는 방식
[resources/static/hello-static.html]
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<title>static content</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
</head>
<body>
정적 컨텐츠 입니다.
</body>
</html>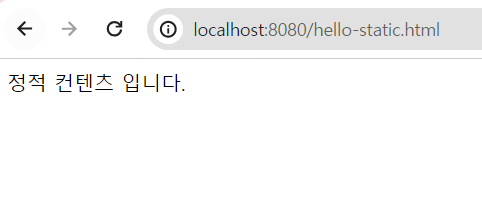
MVC와 템플릿 엔진
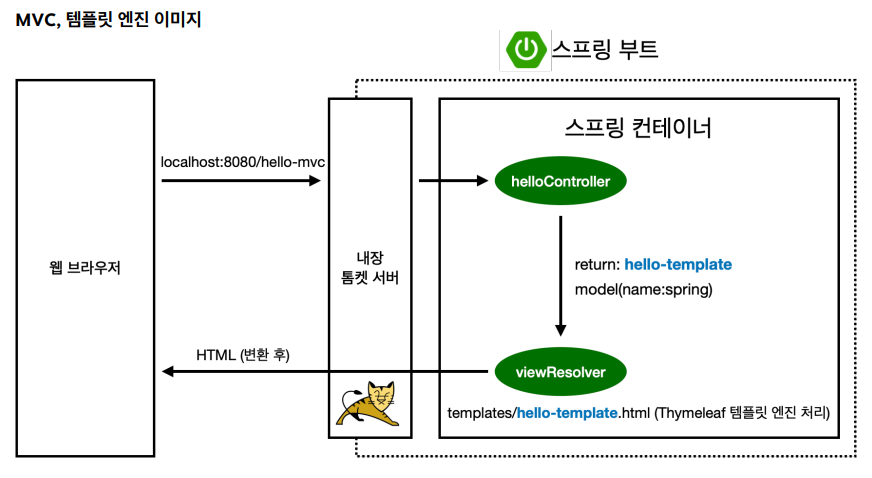
- HTML을 그냥 내려주는 방식이 아니라 서버 내에서 프로그래밍을 하고, HTML을 동적으로 바꾼 뒤에 웹 브라우저에 내려주는 방식
- MVC: Model, View, Controller
Model = 데이터와 비즈니스 로직을 관리
View = 레이아웃과 화면을 처리
Controller = Model과 View로 명령을 전달
Controller
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("hello-mvc")
public String helloMvc(@RequestParam("name") String name, Model model){
model.addAttribute("name", name);
return "hello-template"; //hello-template 파일을 찾아서 렌더링
}
}- @RequestParam: HTTP 요청 파라미터 이름으로 바인딩하는 방법. RequestParam을 사용하면 외부에서 요청한 파라미터를 매우 편리하게 사용할 수 있다.
@RequestParam("가져올 데이터의 이름") 데이터 타입, 가져온 데이터를 담을 변수 - return "hello-template": hello-template 파일을 찾아서 렌더링한다.
View
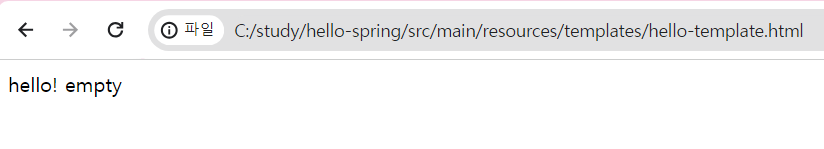
[resources/templates/hello-template.html]
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<body>
<p th:text="'hello ' + ${name}">hello! empty</p>
</body>
</html>- 외부에서 파라미터(name)를 받는다. (@RequestParam)
- 서버 작동 없이 절대경로(C:\study\hello-spring\src\main\resources\templates\hello-template.html)로 실행하면
hello! empty가 출력된다.


API
JSON 형식으로 바꾸어 HTTP Body에 전달하는 방식
JSON이란? (JavaScript Object Notation)
- 자바 스크립트 객체 표기법
- 데이터를 쉽게 교환하고 저장하기 위한 텍스트 기반의 데이터 교환 표준
- JSON은 텍스트 기반이기 때문에 다양한 프로그래밍 언어에서 데이터를 읽고 사용할 수 있다.
- { key : value } : 키(key)와 값(value)의 쌍으로 이루어져 있는 구조
1. @ResponseBody 문자 반환
package hello.hellospring.controller;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("hello-string")
@ResponseBody
public String helloString(@RequestParam("name") String name){
return "hello " + name;
}- @ResponseBody: HTTP(통신 프로토콜)의 body 부에 return값을 직접 넣어주겠다는 의미
- @ResponseBody를 사용하면 ViewResolver를 사용하지 않기 때문에 api를 사용하면 view가 따로 없다.
따라서 '페이지 소스 보기'를 확인해봐도 HTML 관련 코드는 없고 출력된 문자만 보인다. - 템플릿 엔진 vs API
템플릿 엔진은 view라는 템플릿이 있는 상황에서 view를 HTML로 변환하고, API는 데이터를 그대로 내보낸다.

2. @ResponseBody 객체 반환
사실 @ResponseBody는 문자열(String)을 전달하는 경우는 거의 없고, 데이터. 즉, 객체를 요청할 때 주로 사용한다.
package hello.hellospring.controller;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("hello-api")
@ResponseBody
public Hello helloApi(@RequestParam("name") String name){
Hello hello = new Hello();
hello.setName(name);
return hello;
//객체 => Json방식(디폴트)
}
static class Hello{
private String name; //key
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
}- Hello라는 클래스를 만들고, 변수 name과 해당 변수에 대한 Getter/Setter을 생성한다.
- @GetMapping을 통해 url과 연결하고, @RequestParam을 통해 url에서 변수(name)의 정보를 받도록 한다. 그리고 그 정보를 hello.setName을 통해 hello 객체의 변수 name에 대입한다.
- return hello; : 위의 예제처럼 문자를 반환하는 것이 아니라 객체를 반환한다. 객체를 리턴하면 객체가 JSON 방식으로 표현된다. (JSON 방식이 디폴트)
@ResponseBody 사용 원리
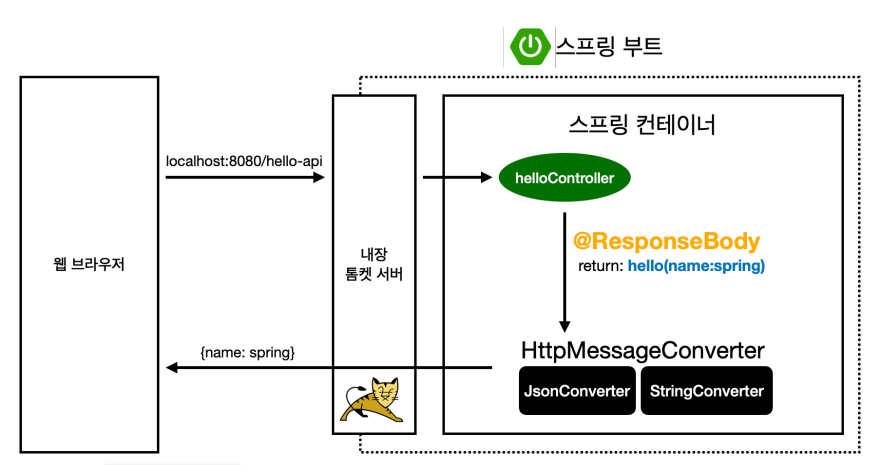
- @ResponseBody의 사용
- HTTP의 BODY에 문자 내용을 직접 반환
- viewResolver 대신에 HttpMessageConverter가 동작
- 기본 문자처리: StringHttpMessageConverter
- 기본 객체처리: MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter
- byte 처리 등등 기타 여러 HttpMessageConverter가 기본으로 등록되어 있음